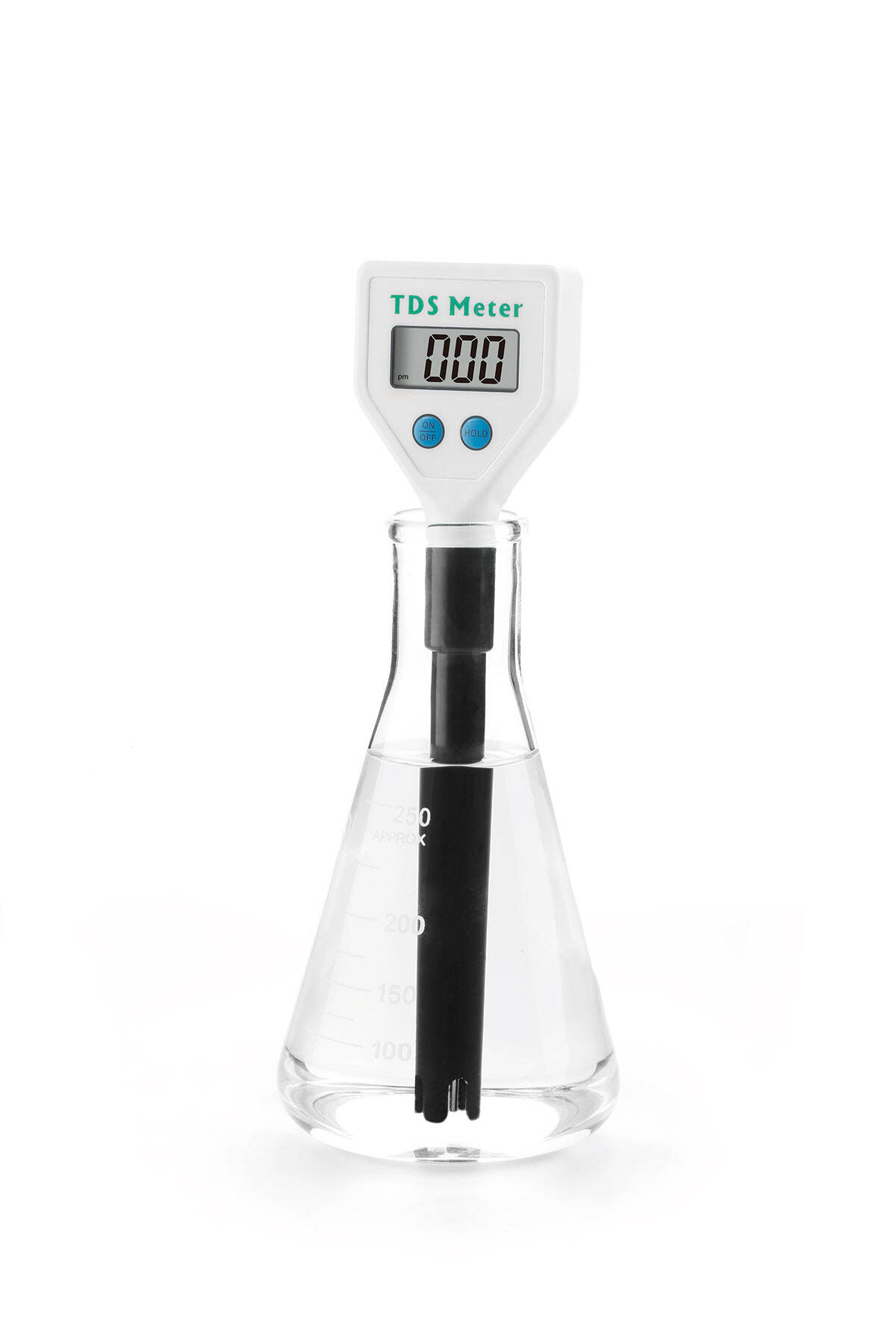
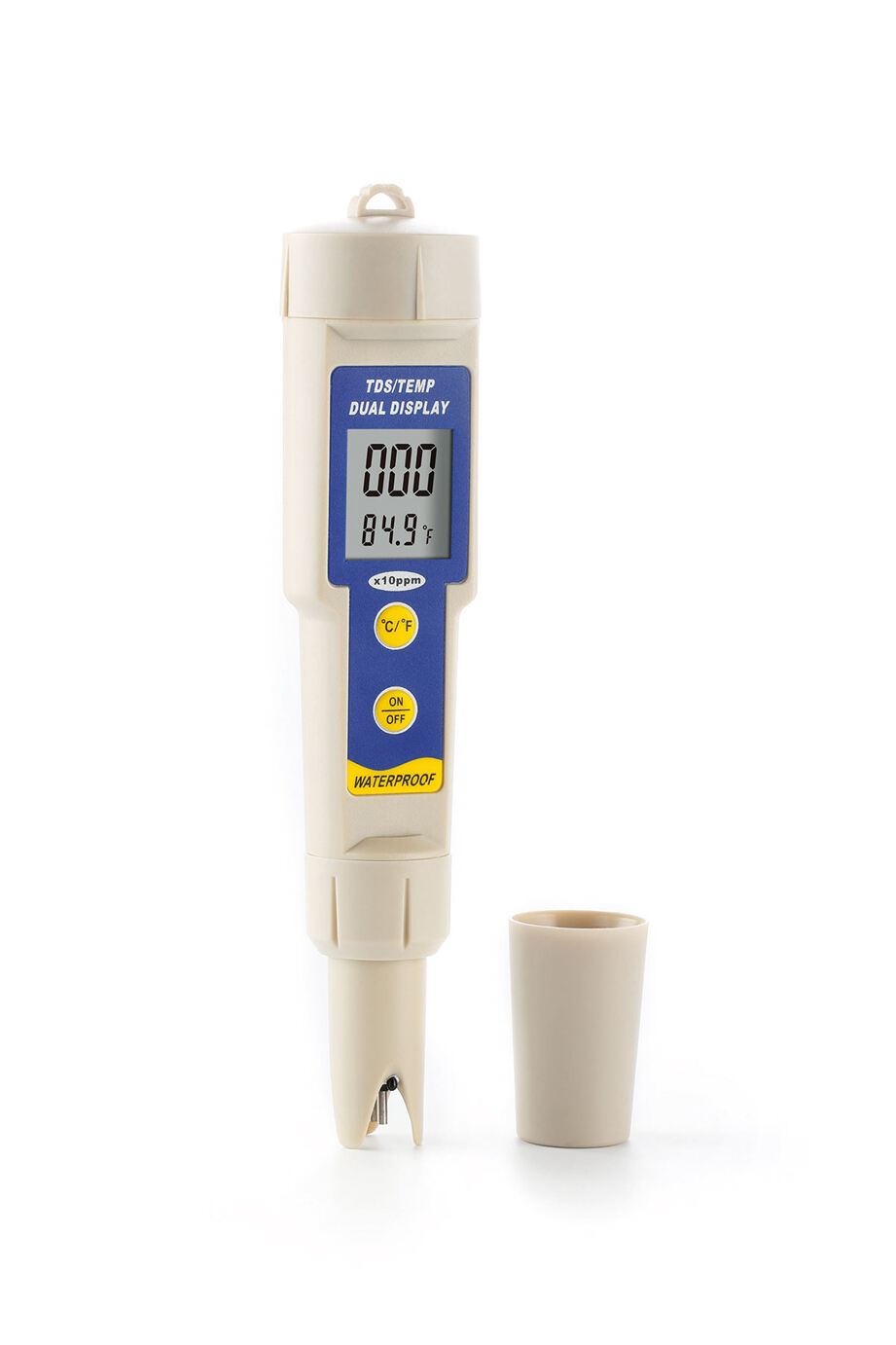
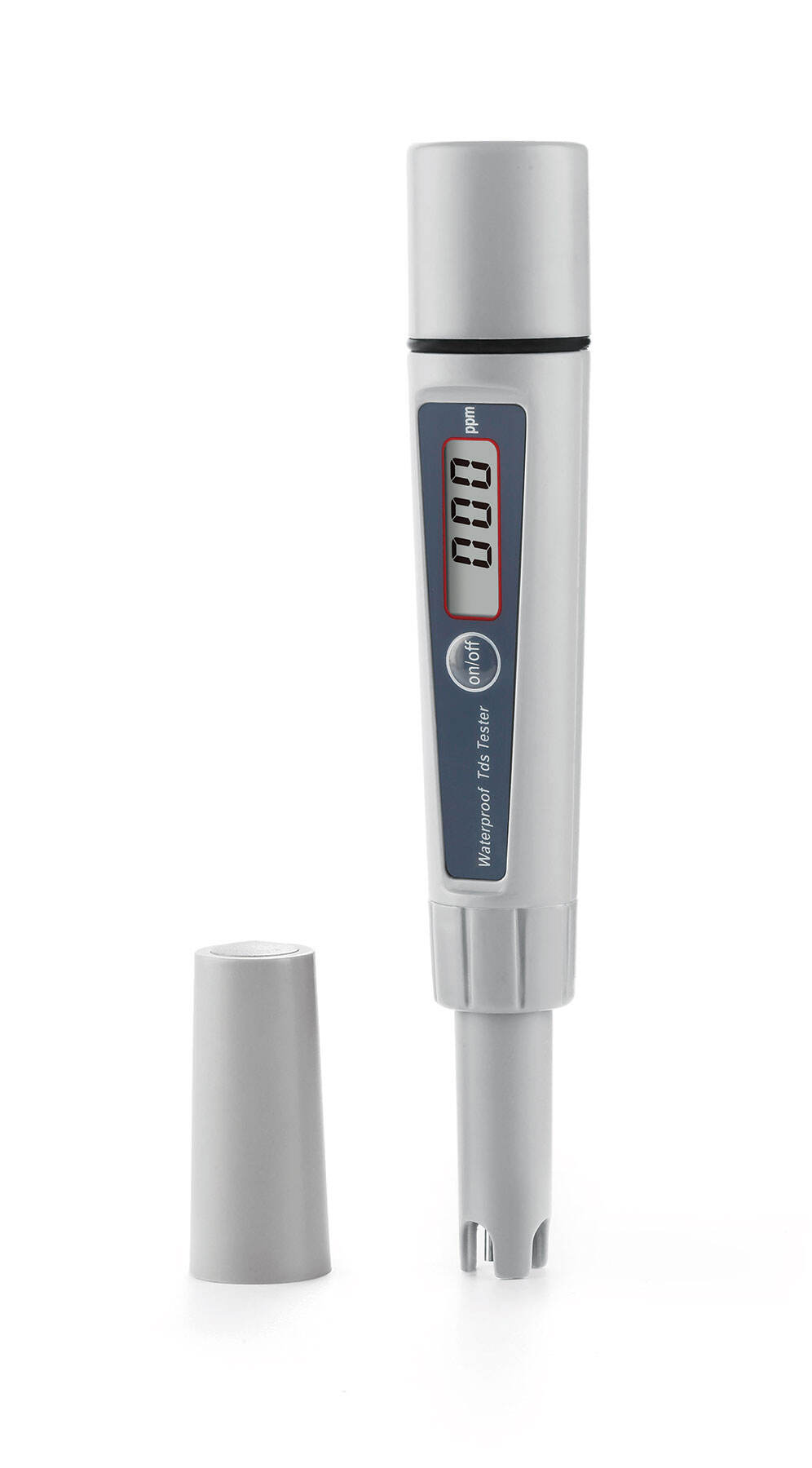
measure tds in water
Measuring TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) in water is a crucial process that determines the concentration of dissolved combined content of all inorganic and organic substances in water. This measurement provides essential information about water quality and its suitability for various applications. The process typically involves using a TDS meter, which measures the electrical conductivity of water and converts it into a TDS reading, usually expressed in parts per million (ppm) or milligrams per liter (mg/L). Modern TDS meters employ advanced microprocessor technology that ensures accurate and rapid measurements, making them indispensable tools in various sectors including water treatment facilities, agriculture, aquaculture, and household water quality monitoring. The measurement process accounts for all dissolved solids, including minerals, salts, metals, cations, and anions. Understanding TDS levels is vital as it impacts water taste, hardness, and overall quality. High TDS levels may indicate the presence of harmful contaminants, while extremely low levels might suggest the water lacks essential minerals. The technology has evolved to include portable devices with temperature compensation features, ensuring accurate readings across different conditions. These instruments have become increasingly user-friendly, offering digital displays and automatic calibration capabilities, making them accessible for both professional and personal use.